In this hashnode blog, I will walk you through the Internet of Things Technology and will share points on the subject. I will take you through basic definitions of IoT, reasons for IoT, IoT Technology, its applications, future scope, and possibility. I will also briefly explain where and how to start. Happy Reading.

This tutorial is also available as a video. Click on the video below or click this link.
What is IoT?
Internetworking of devices, physical objects embedded with sensors, actuators, software, electronics, network connectivity enables these objects to collect and exchange data.
In simple terms :
Network of physical objects or “things” which are interconnected via the “internet”
Brief History of IoT

- 1990: 1 Internet-connected toaster developed by John Roomkeyst
- 1999: Term IoT was coined by Kevin Ashton (Father of IoT).
- 2000: LG announces its first Internet Refrigerator Plans.
- 2008–2009: The IoT was “Born”
IoT Life Cycle
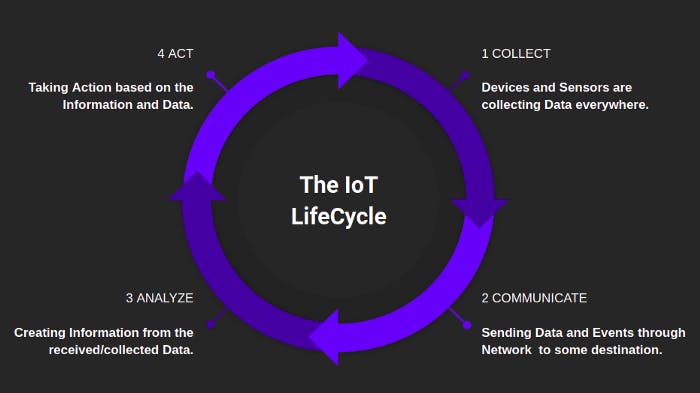
- COLLECT:
Devices and Sensors are collecting Data everywhere. - COMMUNICATE:
Sending Data and Events through Network to some destination. - ANALYZE:
Creating Information from the received/collected Data. - ACT:
Taking Action based on the Information and Data.
How IoT works?
The entire process starts with the devices themselves, such as smartphones, digital watches, electronic appliances which securely communicate with an internet of things platform.
IoT platform collects and combines data from multiple devices and platforms and applies analytics to share the most valuable data with applications to address industry-specific needs.
Why IoT?
Those who hear the term IoT for the first time may have this question, but those who already know the advantages and importance of IoT will react as below.

- Cutting Edge Technology
- 50 billion connected devices by 2025.
- “What was the last piece of technology you purchased that didn’t have Wi-Fi or Bluetooth built-in?”
- Total transparency is available with lesser inefficiencies and greater quality.
- Without human intervention, the machines are able to communicate with each other leading to faster and timely output.
- More information helps to make better decisions.
- Monitoring.
- Saves Money.
- Saves Time.
- Automation on Daily Tasks.
- Better Quality of Life.
IoT Technology
There are many technologies in the market when we talk about IoT, I have listed a few below.
- Bluetooth:
Important short-range IoT communications Protocols / Technology - Zigbee:
ZigBee is similar to Bluetooth and is majorly used in industrial settings. - Z-Wave:
Z-Wave is a low-power RF communications IoT technology that primarily designs for home automation for products such as lamp controllers and sensors among many other devices. - Wi-Fi:
WiFi connectivity is one of the most popular IoT communication protocol - Cellular:
Any IoT application that requires operation over long distances can take advantage of GSM/3G/4G cellular communication capabilities. - NFC:
NFC (Near Field Communication) is an IoT technology. It enables simple and safe communications between electronic devices, and specifically for smartphones, allowing consumers to perform transactions in which one does not have to be physically present. - LoRa Wan:
LoRaWAN is one of the popular IoT Technology, targets wide-area network (WAN) applications.
IoT Data Protocols
- Constrained Application Protocol (CoAP)
- Message Queue Telemetry Transport Protocol (MQTT)
- Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP)
- Data Distribution Service (DDS)
IoT Hardware
Hardware is the core part of any IoT project.

Hardware Components
- Arduino Micro Controllers:
It is basically a smaller board that is plugged into mainboards to improve and increase its functionality by bringing out specific functions or features - Raspberry Pi:
It is a very affordable and tiny computer that can incorporate an entire web server. Often called “RasPi,” it has enough processing power and memory to run Windows 10 on it as well as IoT Core. - Beagle Board:
BeagleBoard is a single-board computer with a Linux-based OS that uses an ARM processor, capable of more powerful processing than RasPi. - Intel’s Galileo:
It’s the first board based on Intel architecture designed to be hardware and software pin-compatible with Arduino shields designed for the Uno R3. - Edison boards:
It is a computer-on-module that was offered by Intel as a development system for wearable devices and Internet of Things devices.
Building Blocks of IoT Hardware
- Thing:
The asset you want to control or monitor. - Data Acquisition Module:
Acquire physical signal and convert it to digital. - Data Processing Module:
The “computer” to process data, perform analytics, store data locally, and other edge computing. - Communications Module:
Communicate with 3rd party systems, either locally or in the cloud
Other Requirements
- IoT Sensors
- Wearable Electronic Devices
- Basic Devices
IoT Software
When someone says, IoT is all about Hardware :|
I will be like below

No, IoT is not all about Hardware, it consists of Software too!
- C Language:
C programming language has its roots in embedded systems — it even got its start for programming telephone switches. - C++ Language:
C++ is the object-oriented version of C, which is a language popular for both the Linux OS and Arduino embedded IoT software systems. - Java:
JAVA is more portable. It is more like a write once and read anywhere language, where you install libraries, invests time in writing codes once and you are good to go. - Python:
Python is an interpreted language, which is, easy to read, quick to learn, and quick to write. Also, it’s a powerhouse for serving data-heavy applications. Its use is slowly spreading to the embedded control and IoT world — especially the Raspberry Pi processor. - B#:
B# was specifically designed for embedded systems, it’s small and compact and has less memory size. - JavaScript:
JavaScript is a very event-driven language, and this makes it ideal for reacting to new data from devices and triggering actions on the devices themselves. - Data Collection:
It is used for data filtering, data security, sensing, and measurement. The protocols aid in decision-making by sensing from real-time objects. It can work both ways by collecting data from devices or distributing data to devices. All the data transmits to a central server. - Device Integration:
This software ensures that devices bind and connect to networks facilitating information sharing. Stable cooperation and communication ensure between multiple devices. - Real-Time Integration:
The input from users serves as potential data for carrying out real-time analysis, making insights, suggesting recommendations to solve an organization's problems, and improve its approach. - Application and Process Extension:
These applications extend the reach of existing systems and software to allow a wider, more effective system. They integrate predefined devices for specific purposes such as allowing certain mobile devices or engineering instruments access.
IoT Companies

Top 5 IoT Companies in the world
- IBM
- Intel
- Microsoft
- Cisco
IoT Applications
IoT is essentially a platform where embedded devices are connected to the internet, so they can collect and exchange data with each other. It enables devices to interact, collaborate and, learn from each other’s experiences just like humans do. Below are a few applications of IoT.
- Smart Home
- Wearables
- Smart City
- Smart Grids
- Industrial Internet
- Connected Car
- Connected Health
- Smart Retail
- Smart Supply Chain
- Smart Farming
Future Scope and Possibility

IoT Impactful Trends
A report has been generated by new research “Top Strategic IoT Trends and technologies through 2023” states the 10 most impactful IoT Trends
- Artificial Intelligence
- Infonomics and data broking
- Shift from intelligent edge to intelligent mesh
- IoT governance
- Sensor Innovative
- Social, legal, and ethical IoT
- Trusted hardware and OS.
- latest IoT User experience
- Innovative on the chip
- New IoT wireless networking technologies
IoT Career Opportunity
Out of many, these are the following career opportunities in the Internet of Things:
- Data analytics
- Network and Structure
- Protection
- Device and Hardware
- Cell and UI development
Types of IoT Jobs
In IoT Career Opportunity, there are various types of IoT jobs that are offered:
- Professional in Sensors and Actuators
- Embedded Programs Engineer
- Software Program Engineering
- Safety Engineering
Where and How to start?

6 Simple Tips for that from my side:
- Gain a deep understanding of sensors
- Focus on the user interface
- Learn JavaScript or Python
- Play with a Raspberry Pi
- Find a community
- Keep your skills cutting edge
Also when we talk about starting with any technology, it totally depends on the way a person learns and wants to develop the skills, following are the ways you can go with.
- Online:
- Udemy
- Coursera
- Lynda
- IoTify
- Books
- YouTube Tutorials
- DIY Projects
- “It’s your choice”
